Researchers discover crucial role of a new enzyme that could be a plant disease breakthrough.
Plant diseases significantly impact agricultural productivity, leading to reduced yields and economic losses. Identifying the pathogens responsible for these diseases is crucial for targeted interventions that can mitigate agricultural impacts.
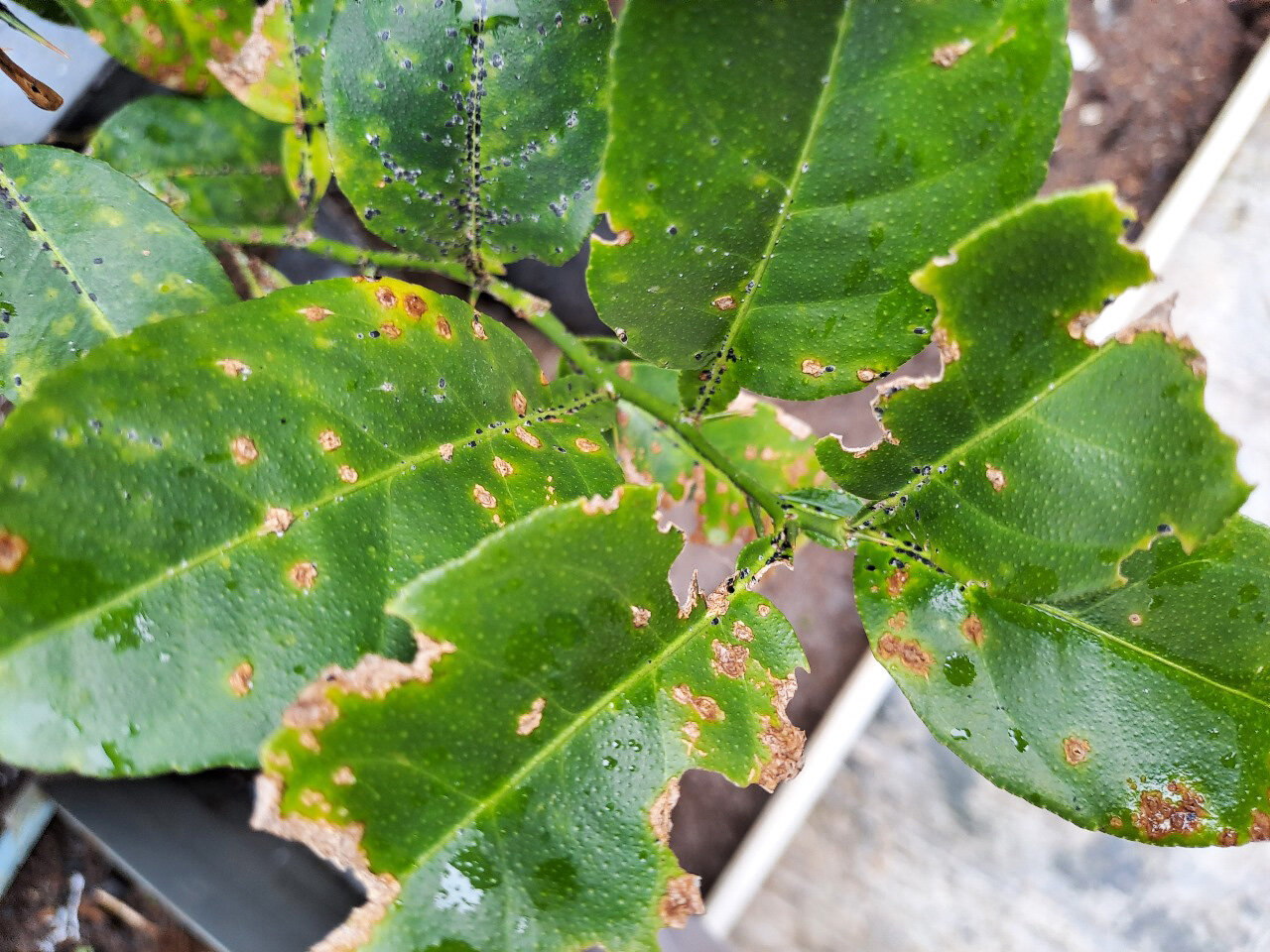
Xanthomonas species are plant pathogens affecting many hosts, including rice, wheat, and tomatoes. They enhance their pathogenicity by using α-1,6-cyclized β-1,2-glucohexadecaose (CβG16α) to suppress essential plant defense mechanisms, such as the expression of pathogenesis-related proteins and the accumulation of callose.
In a recent study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, a team led by Associate Professor Masahiro Nakajima from Tokyo University of Science identified XccOpgD, a glycoside hydrolase (GH186) in X. campestris pv campestris that plays a key role in the biosynthesis of CβG16α. The research team included Sei Motouchi from Tokyo University of Science, principal scientist Shiro Komba from the Institute of Food Research, NARO, and Hiroyuki Nakai from Niigata University.
“Glycan structures are intricate and multifaceted and fulfill diverse crucial roles in nature and organisms. Enzymes synthesize and degrade glycans, exhibiting diverse structures and functions that correspond to the glycan diversity. However, our understanding of these enzymes is still limited, which drives the search for new enzymes with varied new potentials,” Nakajima said in a Tokyo University of Science news release from.
The team conducted biochemical analysis to elucidate the role of XccOpgD in CβG16α biosynthesis. Techniques such as X-ray crystallography were used to unravel the enzyme’s catalytic mechanism and substrate specificity.
These efforts have provided significant insights. XccOpgD belongs to the GH186 family, which is important for regulating bacterial cell wall components. Unlike the first identified GH186 enzymes, XccOpgD exhibits a unique enzymatic mechanism known as anomer-inverting transglycosylation.