The Canola Research Hub at canolaresearch.ca has a user-interactive research database. This article is based on the query “What are some of the factors that impact canola emergence?” with data drawn from a number of canola agronomic studies.
Canola’s yield potential is typically reduced when plant population drops below five-per-square-foot. Aiming for a stand of at least seven healthy, surviving plants per-square-foot allows for some plant mortality due to post-seeding stresses, while maintaining yield potential. Rapid emergence of a dense, uniform stand produces a crop that will compete better with weeds, yield higher and mature earlier and more evenly.
Recent findings confirm previous studies which indicate canola emergence is highly variable, often in the range of 50 to 70 per cent. Seeding depth, seeding speed and uniform planting are among the factors affecting the rate of seed survival.
SEEDING DEPTH
Canola emergence and seedling survival tend to be higher and more uniform with shallow seeding depths. Canola seed sown 1 ‚ÅÑ 2 inch to 1 inch deep into a firm, moist, warm seedbed germinates rapidly with a high emergence percentage.
Neil Harker, research scientist with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC), led a three-year project to study factors affecting canola emergence and quality, including: seed type, seeding speed and seeding depth. In this study, the researchers found that emergence density was greater for canola seeded at a depth of one centimeter (about 1 ‚ÅÑ 2 inch) compared to four centimeters (1 1 ‚ÅÑ 2 inch), with the differences between depths becoming significant with ample moisture.
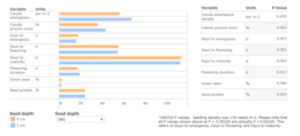
Shallower seeding also comparatively decreased days to emergence, increased canola ground cover, decreased days to flowering and days to maturity, and tended to decrease green seed levels. (See Table 1.)
The higher stand densities that result from shallower seeding depth also create more competitive crop canopies, which can reduce the need for additional herbicide applications, reduce herbicide input costs and reduce selection pressure for herbicide resistance. Relatively high canola stand densities can also improve the ability of canola to successfully tolerate and accommodate biotic and abiotic stress.
STAND DENSITY AND YIELD
Another AAFC study, “Improving Canola Establishment and Uniformity Across Various Soil-Climatic Zones of Western Canada” led by research scientist Yantai Gan, found that uniform and dense plant stands are also important in terms of resulting seed yield.
This experiment compared uniform and non-uniform plant establishment for stands of 100, 80, 60, 40 and 20 plants per square meter (roughly 10, eight, six, four and two plants per square foot). Plants were hand-thinned at the three- leaf stage to create uniform and non-uniform stands.
Overall, uniform planting produced 14 per cent greater seed yield than non-uniform planting at low- to average- yielding sites when plant density was at or below 80 plants per square meter. At high yielding sites, uniform and non- uniform plantings resulted in similar seed yield — as long as plant density was greater than 60 plants per square meter. (See Figure 1.)

Canola yield increases as plant population increases, according to Gan’s study. As plant population went from 20 plants per square meter up to 100 per square meter, yield also increased at all site years.
SEEDING SPEED
Increasing seeding speed will reduce the precision of canola seed placement and thereby reduce the percentage of canola seeds that emerge, no matter which opener type you use, according to a two-year study led by AAFC’s Bob Blackshaw.
The objective of “Management Practices for Optimum Canola Emergence” was to see how opener systems influenced canola seed emergence and how speed influenced seed placement. The study compared six different openers in small-plot replicated trials across different soil types in Western Canada. Additionally, a field-scale study using farmers’ seeding equipment examined the effect of various seeding speeds on canola emergence.
Across all opener types, an increase in seeding speed from four to six miles per hour in the small-plot study resulted in reduced canola emergence in 20 per cent of comparisons in the first year and 33 per cent of comparisons the following year. The results showed little difference in performance between the six openers with all openers usually performing well.

The field-scale study observed seeding tools and emergence results at farms across the Prairies. These trials also indicated a general trend of reduced plant stands with higher seeding speeds. In several cases in Alberta, canola stand was reduced by greater than 20 per cent at higher speeds with expected reductions in yield and quality.
In Saskatchewan, canola emergence over all first-year sites ranged from a low of 23 per cent to a high of 68 per cent, indicating how variable canola emergence can be at the farm level. (See Table 2.)










