ISTA depends on its Technical Committees and its many offerings to members to move global seed testing forward.
The principal objective of ISTA Technical Committees (TCOMs) is to develop, standardise and validate methods for sampling and testing seed quality, using the best scientific knowledge available.
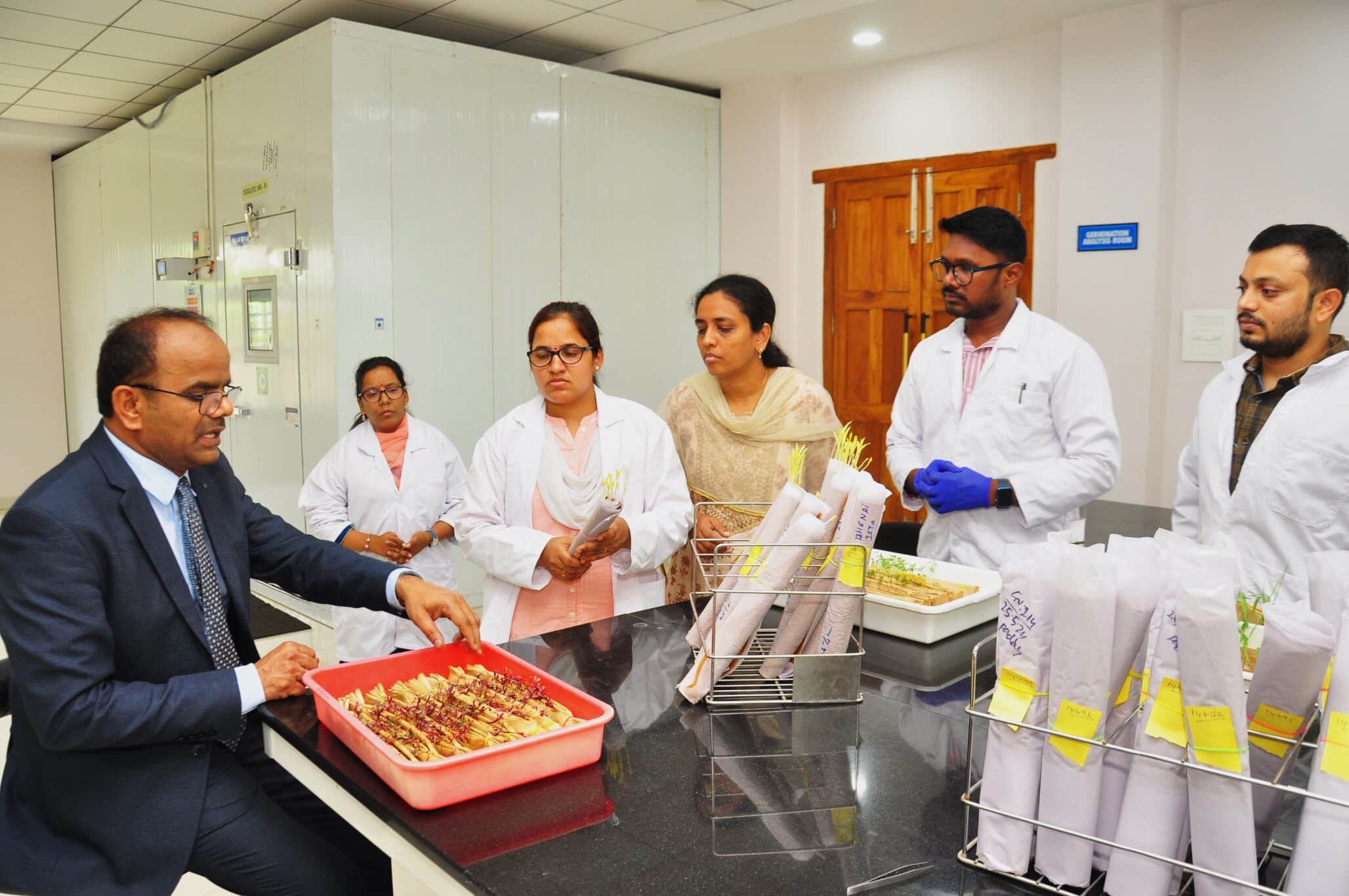
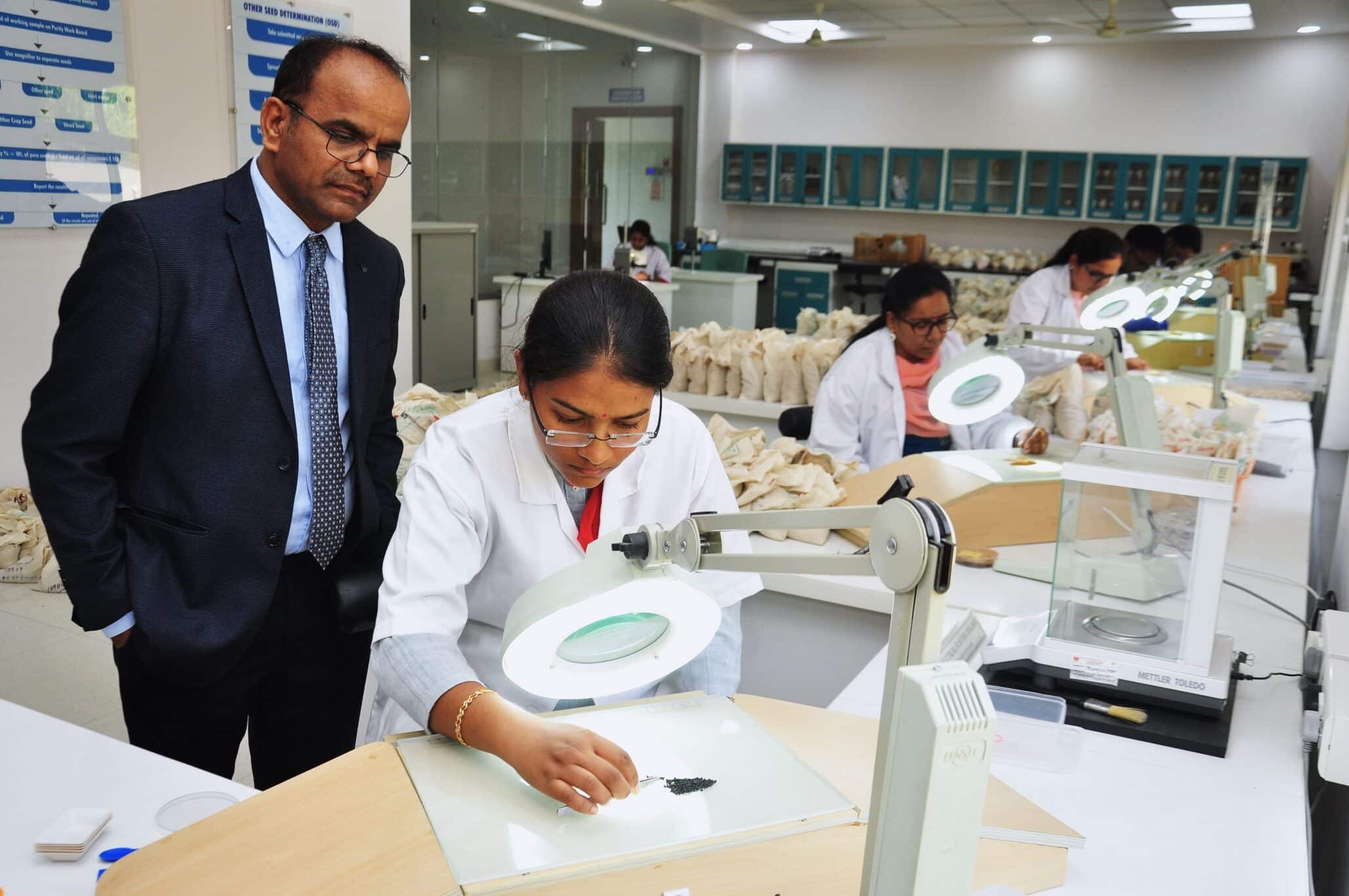
These tasks are subject focused in Technical Committees and Task Forces where scientists, technicians and specialists from all over the world work closely together for the enhancement of seed testing methodologies. The Technical Committees perform comparative studies and surveys in different research fields. They develop and enhance the ISTA International Rules for Seed Testing and ISTA Handbooks on seed methods including sampling, testing and processing seeds, and are responsible for the organization of Symposia, Seminars and Workshops.
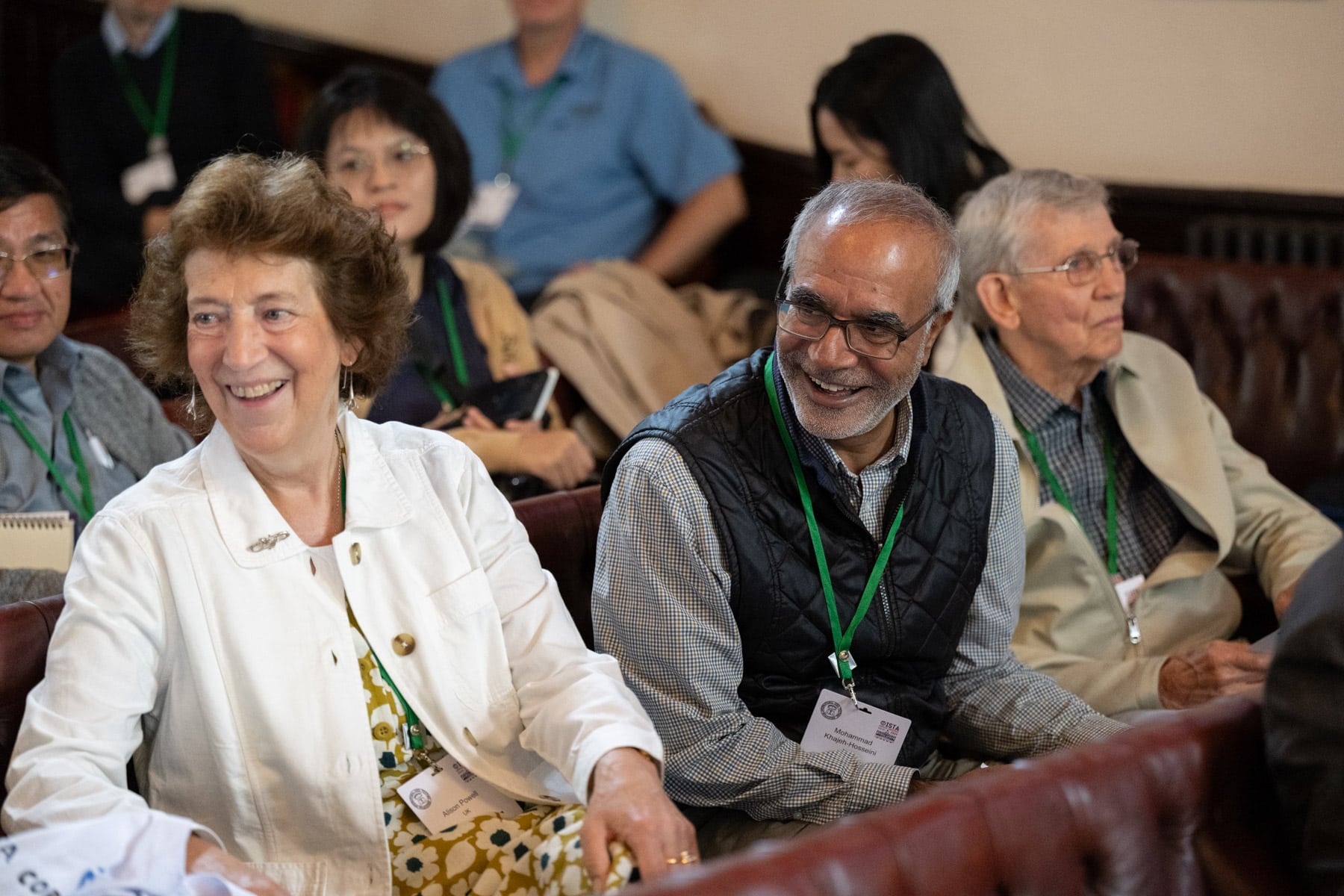
ISTA Technical Committees regularly hold workshops which provide a platform for the exchange of information, experience and ideas.
Who Can Become an ISTA TCOM Member?
Seed scientists and technicians of different research fields of seed science, as well as specialists in seed testing from seed testing laboratories, universities, research institutes and companies from all over the world are welcome to actively participate in the ISTA Technical Committees.
Committees include:
– Advanced Technologies Committee
– Bulking and Sampling Committee
– Flower Seed Testing Committee
– Forest Tree and Shrub Seed Committee
– Germination Committee
– Moisture Committee
– Nomenclature Committee
– Proficiency Test Committee
– Purity Committee
– Rules Committee
– Seed Science Advisory Group
– Seed Health Committee
– Statistics Committee
– Seed Storage Committee
– Tetrazolium Committee
– Variety Committee
– Vigour Committee
– GMO Committee
– Wild Species Working Group and
– Editorial Board of Seed Science and Technology
Use of New Technologies
For methods in the ISTA Rules where technologies can be used that are equivalent to human seed analysts, the technology does not need to be re-validated, but it must be verified for the seed analyst that the technology (equipment) is competent to undertake the analysis. Technology includes any piece of equipment that enables the analysis to be achieved and any operating systems (algorithms, software etc.) that enable the technology to perform its function and, in some cases, provide the final result. Interpretation of the data is still performed by a human analyst.
Research and Knowledge Dissemination
One of the important pillars assuring the uniform application of seed testing methods is training and education. For this purpose, on-site workshops as well as online webinars, held on various aspects of seed testing in which ISTA has experience of several decades, are considered excellent tools.
Experts within ISTA are sources of competence and additionally offer workshops on different aspects of seed testing for training purposes. The lecturers are experienced seed scientists and technicians actively involved within ISTA and considered as experts in their fields.
Seed Testing International (STI)
The ISTA news bulletin, Seed Testing International, is not only read by ISTA Members, which include personal and laboratory members in more than 70 countries/distinct economies but is also distributed to over 1,700 subscribers worldwide.
It includes reports from the ISTA president, Technical Committees and Secretariat. It also includes articles addressing issues of common technical interest and accreditation, reports from various meetings and congresses and regional news covering all issues concerning seed testing in general.
Handbooks
ISTA provides a wide range of handbooks including detailed techniques on all relevant topics in seed sampling and testing methodology. The handbooks are elaborated by ISTA Technical Committees and are excellent tools to improve knowledge and train laboratory staff in different technical areas and facilitate the daily technical work in seed sampling and testing.
Seed Science and Technology
Seed Science and Technology (SST) publishes original papers in all areas of seed quality and physiology related to seed production, harvest, processing, sampling, storage, distribution and testing. The journal is an important tool to promote research in seed science and technology and is a prime source of information for seed scientists and technologists involved in the improvement of seed quality and seed quality control.
The journal was launched in 1973 as a replacement of the Proceedings of the International Seed Testing Association, which was first issued in 1921.
SST is edited by the ISTA Editorial Board and published by ISTA in three issues per volume and year. It is available as open access.
Young@ISTA
Young@ISTA is a special programme initiated by ISTA to attract talented professionals and researchers passionate about seed science and technology. This program aims to ensure the continuity of ISTA’s legacy by engaging individuals who can contribute to the Association’s mission, benefiting their home countries, organisations and personal career development. Through this programme, ISTA seeks to expand its reach and share its knowledge with a wider audience globally.
ISTA Membership
The ISTA membership consists of Personal Members, Associate Members, and over 240 Member Laboratories. The membership is a collaboration of seed scientists and seed analysts from universities, research centers and governmental, private and corporate seed testing laboratories around the world. ISTA values and promotes the diversity of membership, this being the basis for its independence from economic and political influence.
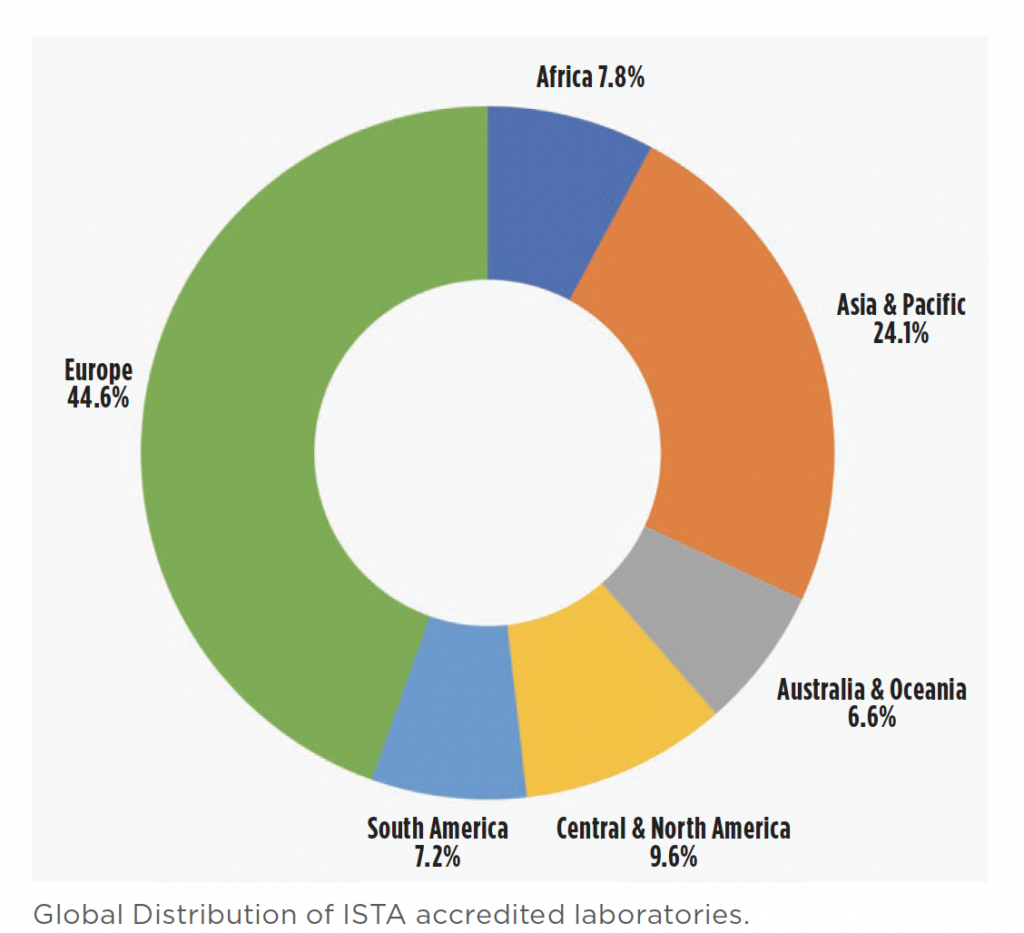
During the last three Trienniums, the ISTA strategy concentrated on growing membership especially in regions where ISTA accredited laboratories were not sufficiently available to the ISTA stakeholders. These areas were mainly Asia, Africa and South America. The special focus was first on Asia. The effort was particularly successful in India. There are currently 34 member laboratories in India, of which nine are accredited. The area is still the quickest growing area in ISTA. All regions mentioned above are still strategic areas for ISTA to grow into the future.